Innovation management
New Product and Process Design and Development
In this unit we investigate the tools that organisations need to introduce to allow them to implement a structured but dynamic Innovation management process.
We examine :
Element 1 : Product Development
- Effective product and service design and its strategic impact on organisations.
- The key stages in the product development process.
- The importance of Cross Functional Concurrent Product Design.
- Techniques for customer delight by reducing product and service variability:
- Kano Model (The 3 levels of customer expectations)
- Taguchi Methods (Robustness through design)
- Poka-yoke (Fail-proofing)
- Quality Function Deployment : (House of Quality)
- Kano Model (The 3 levels of customer expectations)
- Different types of Innovation.
- Open innovation of new ideas by applying :
- Outside-in processes
- Inside-out processes
- Coupled processes
- An introduction to Disruptive Innovation (click for short presentation).
- Protecting intellectual property.
- Implementing a structured but dynamic innovation management process.
- Using break-even analysis as a tool in selecting between alternative products.
- Ecodesign, green design and environmental design : embracing the circular economy.
- Industry 4.0 and the opportunities for Remanufacturing.
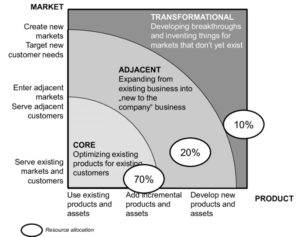
Click on the link below to reveal the differing approaches to innovation.
Element 2 : Process Development
- Identifying different types of processes and explaining their characteristics.
- The 4V’s model of process characterisation and their impact on final product cost.
- Understanding the issues which impact upon the design of product and service processes.
- Linking Product Design & Process Selection to the product life cycle.
- Design for Manufacturing (see details in Lean Tools section).
- Designing Processes to match customer demand profiles:
- Make-to-stock strategy
- Assemble-to-order strategy
- Make-to-order strategy
- Implications of a hybrid approach
- Operational Layout considerations:
- Fixed position (Project)
- Process Orientated (Batch)
- Cell layout (Flexible Batch)
- Product line (Continuous)
- Process design for the circular economy.
- Fixed position (Project)
- Types of plant configurations and their complexities : “A,” “V,” “T,” and “I” configurations.
We have found that delivering these modules in a series of 2 hour slots is the most effective mode of delivery.
After each module, the attendees are required to undertake exercises relevant to the techniques they have been taught.